You can package the assembly into a nuget package, Create a Lib folder inside your solution to hold the nuget package, then, create a nuget.config file to set the package sources to include the Lib folder inside your solution.
The following links contains more details about creating nuget package and hosting it locally:
- https://docs.nuget.org/create/creating-and-publishing-a-package
- https://docs.nuget.org/create/hosting-your-own-nuget-feeds
- https://docs.nuget.org/consume/nuget-config-file
Alternate Method – 1
To run SSIS package you need below DLLs in the code
- Microsoft.SqlServer.ManagedDTS.dll
- Microsoft.SqlServer.PipelineHost.dll
- Microsoft.SqlServer.DTSRuntimeWrap.dll
- Microsoft.SqlServer.DTSPipelineWrap.dll
It is easy to add DLLs in MVC projects, however in asp.net core it needs to be in form of a Nuget package.
So nuget package can be easily created using nuget package explorer. Below is the link
https://docs.nuget.org/create/using-a-gui-to-build-packages
In the nuget package explorer add a lib folder, inside that add a .net folder dnxcore50 and add the above DLLs. Click on tools analyse package and save the nuget.
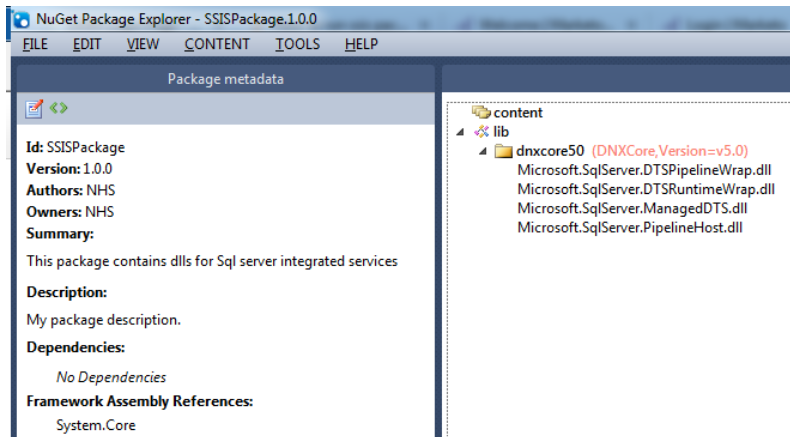
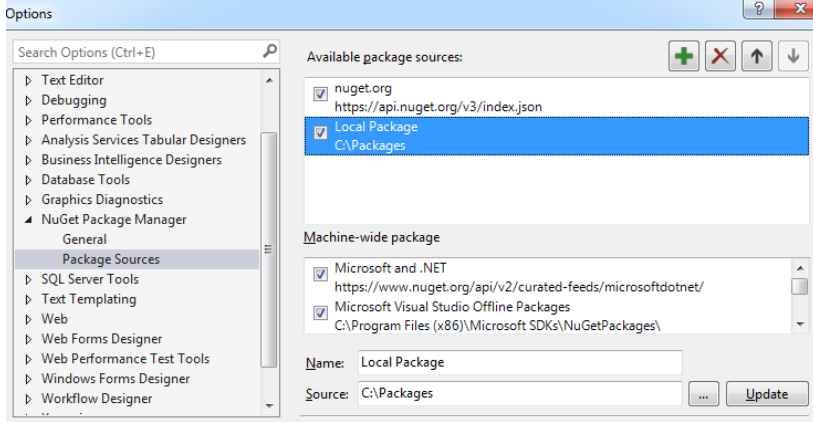
After which you will be able to add the nuget package using nuget package manager and select local package as source
"dependencies": {
"Microsoft.AspNet.Hosting": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.NETCore.Portable.Compatibility": "1.0.1-rc2-24027",
"SSISPackage": "1.0.0"
}
"frameworks": {
"netcoreapp1.0": {
"imports": [
"dotnet5.6",
"portable-net45+win8",
"dnxcore"
]
}
}
After which you will be able to use code to run SSIS package similar to MVC projects.
Application app = new Application();
Package package = null;
try
{
package = app.LoadPackage(@"C:\Files\Package.dtsx", null);
Variables vars = package.Variables;
vars["status"].Value = "ACTIVE";
DTSExecResult results = package.Execute();
}
catch
{
return false;
}
finally
{
package.Dispose();
package = null;
}
Alternate Method – 2
You may now reference the dlls ( one from each) directly in your .net core project from the below locations to run ssis packages now
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\assembly\GAC_MSIL\Microsoft.SqlServer.ManagedDTS
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\assembly\GAC_MSIL\Microsoft.SqlServer.PipelineHost
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\assembly\GAC_64\Microsoft.SqlServer.DTSRuntimeWrap
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\assembly\GAC_MSIL\Microsoft.SqlServer.DTSPipelineWrapyou no longer need to create a nuget package
Reference
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/38791987/how-to-run-ssis-package-in-asp-net-core-application