Dataset is an in-memory representation of a database relationship. Data Tables are individual tables that can be joined with Data relation objects.
Let’s go through an example of a tenant and his/her maintenance request;
Create a Dataset;
//create dataset
DataSet serviceRequest = new DataSet();
Create tenant table
//create tenant table
DataTable tenant = new DataTable();
tenant.Clear();
//add columns
tenant.TableName = "tenant";
tenant.Columns.Add("tenantID");
tenant.Columns.Add("Name");
tenant.Columns.Add("AptNumber");
//add rows
DataRow rowT = tenant.NewRow();
rowT["tenantID"] = "A1";
rowT["Name"] = "khan";
rowT["AptNumber"] = "1";
tenant.Rows.Add(rowT);
//Add this table to data set
serviceRequest.Tables.Add(tenant);
Create request table
//create request table
DataTable request = new DataTable();
request.Clear();
//add columns
request.TableName = "request";
request.Columns.Add("requestID");
request.Columns.Add("tenantID");
request.Columns.Add("description");
//add rows
DataRow rowR = request.NewRow();
rowR["requestID"] = "1";
rowR["tenantID"] = "A1";
rowR["description"] = "air conditioner does not work";
request.Rows.Add(rowR);
//add this table to data set
serviceRequest.Tables.Add(request);
Create relationship
//create relationship
DataRelation relation;
DataColumn tenantColumn = serviceRequest.Tables["tenant"].Columns["tenantID"];
DataColumn requestColumn = serviceRequest.Tables["request"].Columns["tenantID"];
relation = new DataRelation("relation", tenantColumn, requestColumn);
//assign relation
serviceRequest.Relations.Add(relation);
Create LINQ query to read data;
//simple LINQ query
var maintenanceData = (from x in serviceRequest.Tables["tenant"].AsEnumerable()
join y in serviceRequest.Tables["request"].AsEnumerable()
on x.Field<string>("tenantID") equals y.Field<string>("tenantID")
select new
{
TenantID = x.Field<string>("tenantID"),
RequestID = y.Field<string>("requestID"),
Description = y.Field<string>("description")
}).ToList();
Here is the output of this LINQ query;
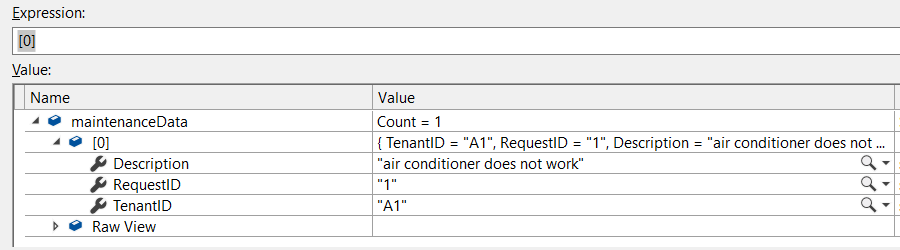
If we are going to add a new column in request table, for example AllowToEnterApt. We can use foreach loop to update the values in this column;
serviceRequest.Tables["request"].Columns.Add("AllowToEnterApt");
foreach (DataRow row in serviceRequest.Tables["request"].Rows)
{
row["AllowToEnterApt"] = 1;
}